A customer value proposition can be defined and assessed through the development of the Customer Value Assessment (CVA). The Customer Value Assessment is a set of criteria across four categories that capture a customer’s wants, needs or expectations. Using these criteria, organizations gain insight into the customer’s perception of their organization. The four CVA categories include Solutions, Responsiveness, Economics, and Relationship.
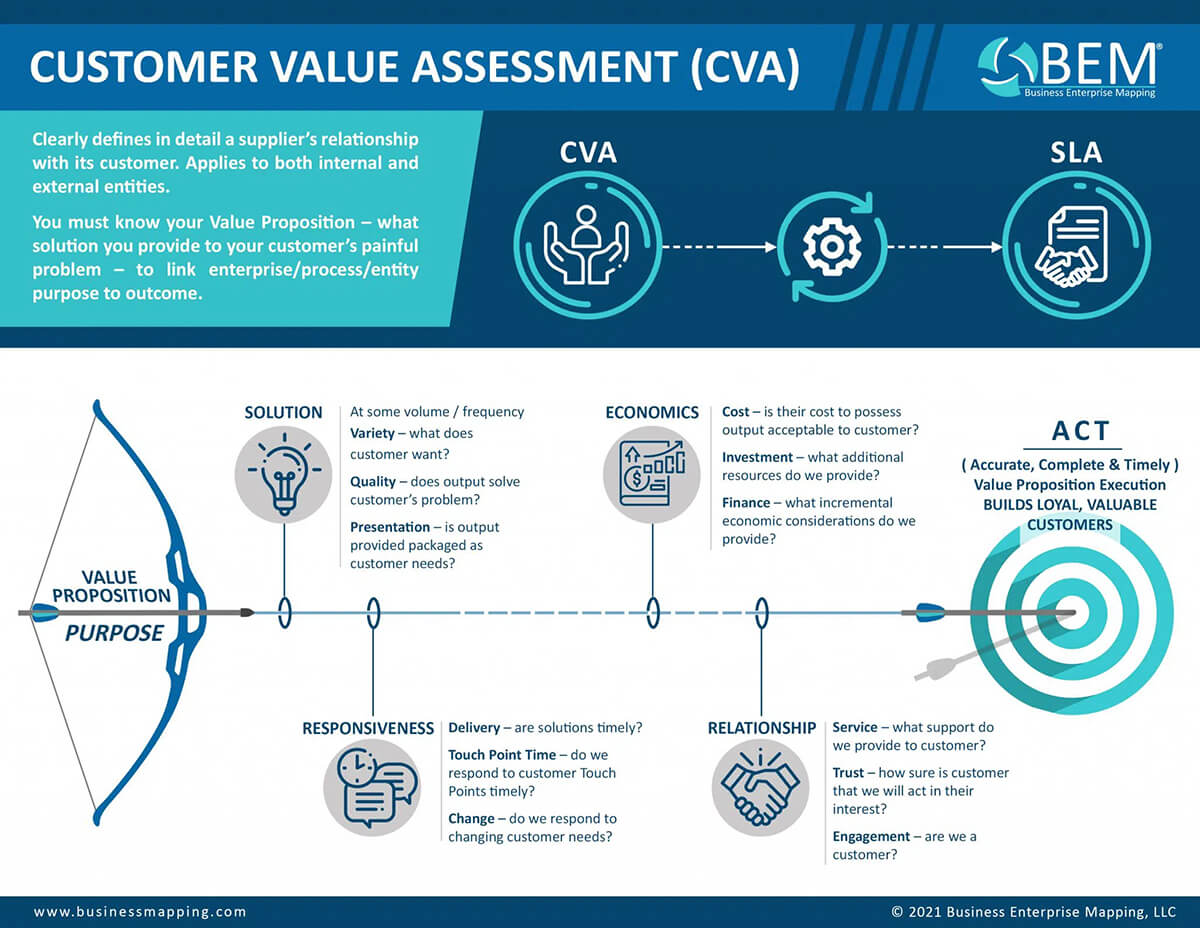
Solutions - Does the organization offer solutions that customers prefer?
Solutions represent the core products and services provided by the organization to fulfill its purpose. Ideally, solutions would successfully solve the customer’s problem, or fully satisfy the customer’s want or need. Three elements further define this category.
- Portfolio - the offerings of products and services intended to fulfill the customer’s wants or needs.
- Characteristics - the intended function that the provided products and services fulfill.
- Presentation - the format, packaging, supporting information and method of delivery of the products and services provided.
Responsiveness - Does the organization provide what customers want, when they want it?
Responsiveness represents the customer-desired time for all transactions. This can be expressed in several ways, such as time to respond, availability, scheduled when convenient, regularly scheduled and frequency. Three elements further define this category.
- Delivery - the time to deliver the provided solutions.
- Transactions - the time to respond to each customer interaction.
- Inquiry – the time to respond to market and customer required changes.
Economics – Does the organization provide attractive financial value?
Economics represents the customer’s financial considerations when evaluating the purchase of products and services. Three elements further define this category.
- Cost - the total cost to the customer of usage, consumption or ownership of the product or service provided.
- Investment - the additional or incremental tangible value provided with or without cost to the customer.
- Finance - the terms, risk, profit contribution and other economic considerations considered by the customer in acquiring the products or services.
Relationship – Is the organization important to the customer?
Relationship defines the customer’s perception of the organization that provides solutions. Three elements further define this category.
- Service - the assistance provided to the customer in support of the core solution and transactions. Service is intended to improve the customer’s experience by assisting the customer to meet their needs.
- Trust - the level of confidence that the customer has that the organization can be trusted, requiring knowledge, intention, and capability.
- Involvement -the level of engagement the customer desires from the organization, such as weekly reviews, annual senior leadership meetings, or even no contact at all. Ideally, an organization would be considered a valuable partner to the customer’s business.
The Customer Value Assessment defines customer relationships.
The CVA can be used to accomplish several key objectives:
- Define customer types
- Determines what each customer type requires
- Assesses if the organization gives customers what they want
- Examines the gaps and their causes
- Determine the changes necessary to close those gaps
Further Reading: THE PERIGON METHOD

